
Through Deskera CRM, you can focus on contact and deal management, activity management, knowledge base management and tracking of communications to inventory management all in one platform with all the real-time updates. Deskera’s inventory management software enables you to stay on top of your stock levels at all times and absorption costing fulfill your customer orders with confidence. Meeting the customers’ demands quickly and efficiently will keep them happy and coming back for more. Numerous organizations, including FASB (USA), ASG (UK), and ASB (Australia), have acknowledged it for the purpose of establishing external reporting and inventory value (India).
Absorption Costing vs. Variable Costing
In summary, absorption costing provides a full assessment of production costs for inventory valuation, while variable costing aims to show contribution margin and provide internal reporting. Most companies https://www.bookstime.com/ use absorption costing for external financial reporting purposes. By allocating fixed overhead to units produced, absorption costing provides a more complete assessment of production costs.
- For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online.
- Absorption costing, also called full costing, is what you are used to under Generally Accepted Accounting Principles.
- Indirect costs are those costs that cannot be directly traced to a specific product or service.
- The other main difference is that only the absorption method is in accordance with GAAP.
- The accuracy of product costs under this technique is contingent on the proper allocation of overhead costs.
Absorption Costing Formula:
The variable cost per unit is $22 (the total of direct material, direct labor, and variable overhead). The absorption cost per unit is the variable cost ($22) plus the per-unit cost of $7 ($49,000/7,000 units) for the fixed overhead, for a total of $29. If the 8,000 units are sold for $33 each, the difference between absorption costing and variable costing is a timing difference. Under absorption costing, the 2,000 units in ending inventory include the $1.20 per unit share, or $2,400 of fixed cost.
Calculating Ending Inventory Using Absorption Costing
- Absorption costing is a method of costing that includes all manufacturing costs, both fixed and variable, in the cost of a product.
- Absorbed overhead is manufacturing overhead that has been applied to products or other cost objects.
- Variable costing cannot be utilized in financial reporting under accounting standards like IFRS and GAAP.
- Therefore, the methods can be reconciled with each other, as shown in Figure 6.17.
- By including fixed overhead costs in product costs, it presents a fuller, incremental view of profitability.
- Advocates of absorption costing argue that fixed manufacturing overhead costs are essential to the production process and are an actual cost of the product.
Therefore, fixed overhead will be allocated by $ 1.50 per working hour ($ 670,000/(300,000h+150,000h)). Net income is derived by subtracting all expenses (COGS and operating expenses) from total sales revenue. Absorption costing is viewed as the cornerstone of cost accounting in manufacturing businesses and plays a pivotal role in financial decision-making and performance evaluation.
- Therefore, all fixed manufacturing expenses are deducted as they are incurred.
- Figure 6.11 shows the cost to produce the 10,000 units using absorption and variable costing.
- This is because variable costing will only include the extra costs of producing the next incremental unit of a product.
- Absorption costing recognizes the significance of factoring in fixed production expenses when evaluating product costs and pricing strategies.
(f) Unsold stock-related fixed costs pass onto the next accounting period in part. (a) The finished product absorbs all manufacturing costs, whether direct or indirect. Period costs include all overheads related to the organization, sales, and distribution.
Calculating Total Cost: Absorption Costing Method
Under absorption costing, companies treat all manufacturing costs, including both fixed and variable manufacturing costs, as product costs. Remember, total variable costs change proportionately with changes in total activity, while fixed costs do not change as activity levels change. These variable manufacturing costs are usually made up of direct materials, variable manufacturing overhead, and direct labor. The product costs (or cost of goods sold) would include direct materials, direct labor and overhead. Absorption costing is an inventory valuation method that allocates all manufacturing costs, including both variable costs and fixed overhead costs, to the units produced. This means that inventory is valued to include both direct costs of materials and labor as well as a portion of fixed manufacturing overhead costs.
- The key difference from variable costing is that fixed production costs are included in the inventory valuation and expense recognition under absorption costing.
- Absorption costing is in accordance with GAAP, because the product cost includes fixed overhead.
- Under Absorption Costing, we consider variable and fixed selling & general administrative expenses as period costs, and we expense them in the period they’re incurred; we do not include them in the cost of production.
- Throughout the production process, you’ll need to calculate usage for activities.
Holding management accountable for expenses it has no control over is not feasible. Now that we have the Absorption Cost calculated and we know that the management is looking for a mark-up of 35%, we can calculate the selling price. The difference in the methods is that management will prefer one method over the other for internal decision-making purposes.

What you will learn to do: distinguish between variable costing and full absorption costing
Since ABS costing considers fixed production overhead as a product cost, all goods ending in inventory (i.e., unsold at the end of the period) constitute a component of those expenses as an asset on the balance sheet. In a scenario where all fixed manufacturing overhead would be expensed for the relevant period under variable costing. The costs here include raw materials and labor directly tied to production, variable, and fixed overheads. In contrast to the variable costing method, every expense is allocated to manufactured products, whether or not they are sold by the end of the period. This is important for financial reporting and decision-making because it takes into account both variable and fixed production costs. When it comes to making managerial decisions, absorption costing is ineffective.
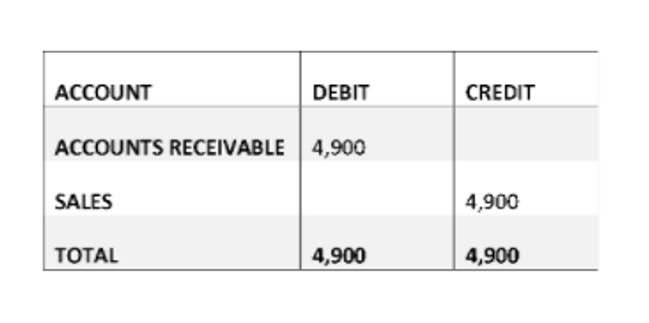
The other main difference is that only the absorption method is in accordance with GAAP. This enables businesses to make informed decisions and maintain accurate financial records in a complex manufacturing environment. (d) With the help of absorption rate, manufacturing expenditures that aren’t related to a single product get distributed.
Recent Comments